What is a Work Order?
A work order is a documentation of a job or service request that is issued to track and monitor the status of the request which is raised by either a customer or internal stakeholder.
Companies that provide field service, or operate in industries that involve regular inspection or maintenance of equipment or machinery deal with work orders frequently.
These can be either a new request, a monthly scheduled repair task, performing preventive maintenance, or re-visiting an already completed job because of a new issue.
Teams Involved in Handling a Work Order
- Work requestor: The work requestor is the person or team who submits a work request. As mentioned before, this is the result of a customer request. But work orders can also be auto-generated for a follow-up on an already completed task for auditing purposes.
- Work approver: This would be a specific person or team that handles the approval and assignment of maintenance requests in the case of equipment management, or it could be a customer service or dispatch team that undertakes the same role for work order requests from clients.
- Field technicians: This group consists of maintenance engineers, field technicians, or repairmen who are on the field, executing the actual tasks associated with the work orders.
Here’s a Preview of Freshdesk in Action
Elements of a Work Order Document
- Order id: The unique identification number assigned to every work order request
- Title: The name given to the work order. E.g., Heating issue.
- Date of request: Date the work order was raised
- Problem Description: A short 3-4 line brief about the problem or request. E.g., Cooling unit of the engine not running at full power.
- Asset: This field specifies which asset or assets need attention or repair, For example, An AC unit or Material Handler in a warehouse.
- SLA: The agreed upon, or promised time to completion of the maintenance work order by Service teams & technicians.
- Cost estimation: The exact overhead including all expenses related to the work order
- Category: What type of work order is defined here. It varies based on the company and industry.
- Status: The current status of a work order. “Assigned,” “In progress,” “Re-opened,” “Completed” are common statuses used.
- Priority: Priority of a work order usually labeled as high, medium or low
- Customer info: Details about the customer or stakeholder who raised the initial service request or issue. Includes name, phone number, email address, and location information
- Technician assigned: Name and other details of the technician assigned to the work order request.
- Additional Documents: Supporting documentation required for the tasks
What are Work Orders Used For?
Work orders are an integral part of an organization’s workflow when it comes to resolving issues. Here are the different ways work orders help organize maintenance operations:
-Request status: Using work requests as a reference point helps track the progress of a request from task creation until completion. It provides all the relevant information about the problem while also helping field technicians get complete context on the job at hand.
-Scheduling resources and tools: Since a work order consists of essential details about a service request, it can also be a source of information for both dispatch teams and technicians, of the necessary resources – including new parts and tools – that would be needed to complete the task.
-Documentation and prioritization: Work orders are used in creating a detailed record of the activities and resources used during a service request. Work order information also helps dispatch teams determine which tasks need to be prioritized.
What is the Work Order Process?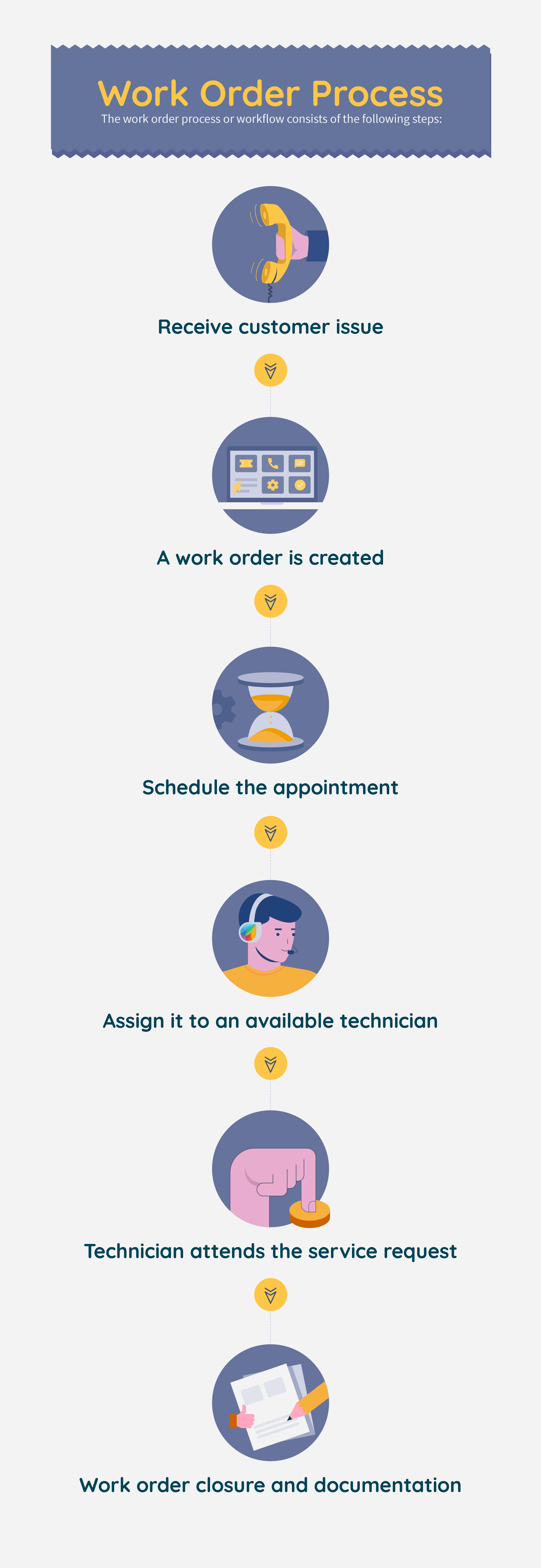
The work order process or workflow consists of the following steps:
- Receive customer issue or maintenance request: When a problem arises, the customer or the stakeholder sends the request to the support team or dispatch team describing the issue.
- A work order is created: Once the request is received, a work order is generated with all the details of the task to be performed.
- Schedule the appointment: The job order is scheduled for a particular time, and the maintenance team is notified of the same.
- Assign it to an available technician: The maintenance team assigns the task to an available technician or field worker based on proximity to the location and their workload.
- Technician attends the service request. The field technician will travel to the customer location or the plant site to inspect the problem. They perform the necessary repairs on the equipment and document the process for validation.
- Work order closure and documentation: Once the job is completed, the technician informs the maintenance team. They will change the status of the work order to ‘complete’ and tell the support team as well as the customer.
Work Order vs. Purchase Order
A work order is used to capture all the details of a service request and track its progress.
A purchase order, on the other hand, is a document authorizing the procurement of an asset or resource required by the team that raised the request.
In maintenance management, these two come together when it involves ordering a spare part or a new unit to complete the work request.
Challenges of Maintenance Work Order Management
Work orders are a beneficial way of capturing the essentials of any maintenance request, but managing several such tasks becomes challenging. Here are two fundamental difficulties organizations face in executing work order requests:
- Tracking work orders using Excel or paper-based systems is inefficient
In a digital-first world, it is no longer feasible to continue using spreadsheets or printing out a work order form. It takes longer to create and update tasks, and if there are errors or wrongly printed information, it requires a do-ever. All of this leads to inefficiencies and avoidable waste of time, and money Maintenance teams and technicians find it a hindrance to do their jobs efficiently because of such manual tasks and re-works.
- Coordination between maintenance teams and field workers is difficult.
There needs to be an established line of communication between dispatch teams and technicians to consistently keep the other side updated on the status of the work request. Without a work order management system, organizations have to resort to either email or phone, which means a lot of calls and interruptions. This leads to a longer maintenance cycle because collaboration for any small change requires manual communication.
Advantages of using Work Order Management Software
Here are just a few of the many ways work order software makes life easier for service teams:
Bringing service teams and field teams on the same platform

Freshdesk’s Work Order Management software brings your dispatch teams and field engineers on the same platform. This way, coordination is made extremely simple. Any new task-related information can be updated within the system and made accessible to the right people.
Simplified task management & automated workflows

Details about any service order or job order can be quickly recorded and updated within Freshdesk. You can also create custom fields based on the type of service order you raise. With automated workflows, you can create condition-based triggers that automatically change the status or priority of a task in real-time eliminating the need for manual action
Scheduling dashboard to manage appointments

Our robust scheduling dashboard makes viewing, assigning, and managing service tasks and technicians very straightforward. You can see all appointments and every technician’s calendar in one single view and use simple drag and drop controls to schedule and update work orders on the dashboard.

Work Order Management in Action – An Example
To understand the workflow of a work order, we look at how a company managed its job request before and after implementing software:
A high growth logistics company faced the following challenges when managing service requests
- Using email and phone, which became cumbersome to handle the high volume of queries.
- Escalations also increased due to slow response times, which meant more work for the technicians.
Solution:
- By implementing an integrated work order software, they were able to unify support and service teams resulting in faster collaboration and higher efficiency.
- Using automation, several workflows were executed automatically, such as updating the status of a job order: this reduced resolution times and improved technician productivity.
Simplify your Field Operations
Work order management is a critical function for field organizations and plays an integral part in improving maintenance systems and processes. Implementing software to digitize these processes dramatically reduces the complexity of managing work orders and, most importantly, improves customer experience.
Looking For Startup Consultants ?
Call Pursho @ 0731-6725516
Telegram Group One Must Follow :
For Startups: https://t.me/daily_business_reads